
During the delay, cross winds exceeded return-to-launch-site limits at KSC's Shuttle Landing Facility. The fixture was sawed off and an attaching bolt drilled out before closeout was completed. The launch was delayed 24 hours again when the ground servicing equipment hatch closing fixture could not be removed from the orbiter hatch. Prediction of unacceptable weather at the Kennedy Space Center (KSC) led to the launch being rescheduled for 9:37 a.m. The launch was postponed another day when launch processing was unable to meet the new morning lift-off time. To utilize Casablanca (not equipped for night landings) as alternate TAL site, T-zero was moved to a morning lift-off time. Launch was reset for January 25 because of bad weather at the transoceanic abort landing (TAL) site in Dakar, Senegal. The launch was re-scheduled for January 22, however, the date slipped to January 23, then January 24, due to delays in mission 61-C. The November launch date slipped due to delays. The astronaut crew were assigned in January 1985, however, the launch was rescheduled to late November 1985 due to changes in payloads. Shuttle Mission 51-L was originally scheduled for July, 1985. Space Shuttle Challenger Mission 51 L History Halley's Comet Experiment Deployable, a free-flying module designed to observe tail and coma of Halleys comet with two ultraviolet spectrometers and two cameras. Spartan satellite was to have been deployed into low Earth orbit using the remote manipulator system. Spartan satellite that would be deployed into orbit carrying special instruments for the observation of Halley's Comet. The satellite would have supported communications with the Space Shuttle and up to 23 other spacecraft. Tracking Data Relay Satellite-2 (TDRS-2): a NASA communications satellite that was to have been placed in a geosynchronous orbit with the aid of a booster called the Inertial Upper Stage. The payloads flown on Space Shuttle Challenger Mission 51-L included: The Challenger cargo included two satellites in the cargo bay and equipment in the crew compartment for experiments that would be carried out during the mission. Christa McAuliffe - Payload Specialist 2 The crew of Space Shuttle Challenger consisted of 7 astronauts: She was selected from more than 11,000 applicants. Christa McAuliffe, a high school teacher from New Hampshire was to be the the first civilian in space.
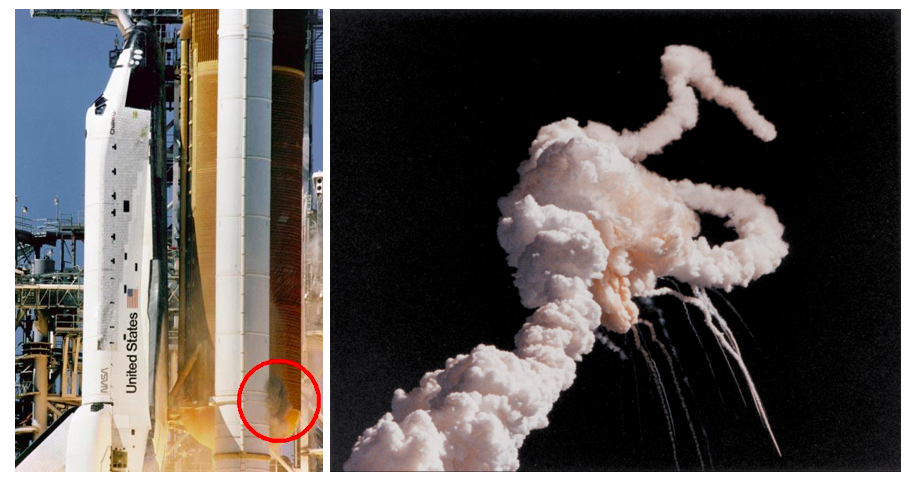
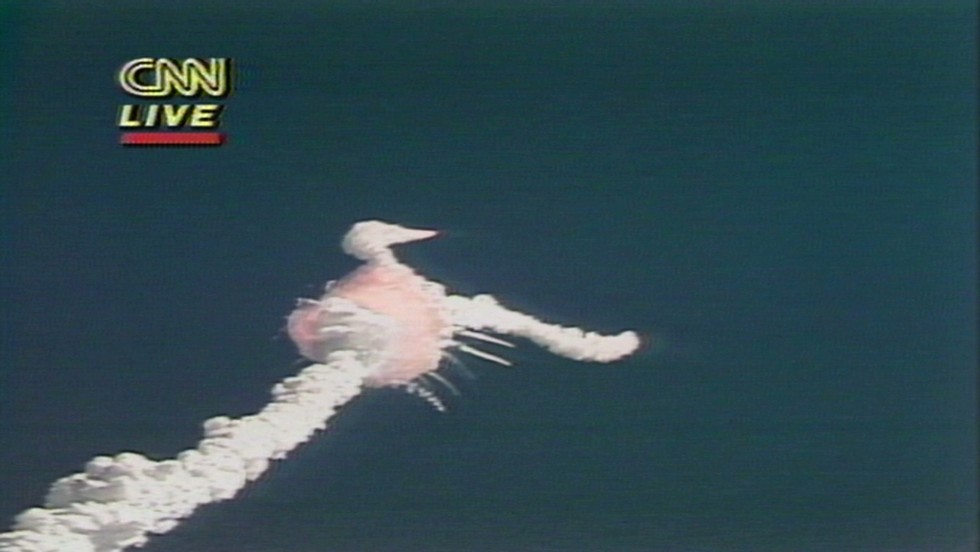
This mission was highly publicized because it was the first time a school teacher was allowed to travel in space. It was launched from Pad 39B at Kennedy Space Center in Florida at 11:38am EST. The Space Shuttle Challenger Mission (Flight STS-51L) was the 25th Space Shuttle mission and the 10th launch of the Space Shuttle Challenger. 1.1 Space Shuttle Challenger Mission 51 L History.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
